Introducing the
Qore Data Factory
The combination of automation and researchers allows us
to reach up to 99% data accuracy for all our published data
The processes of extracting data from diverse sources & integrating it into repositories that are many more times more valuable than the independent parts
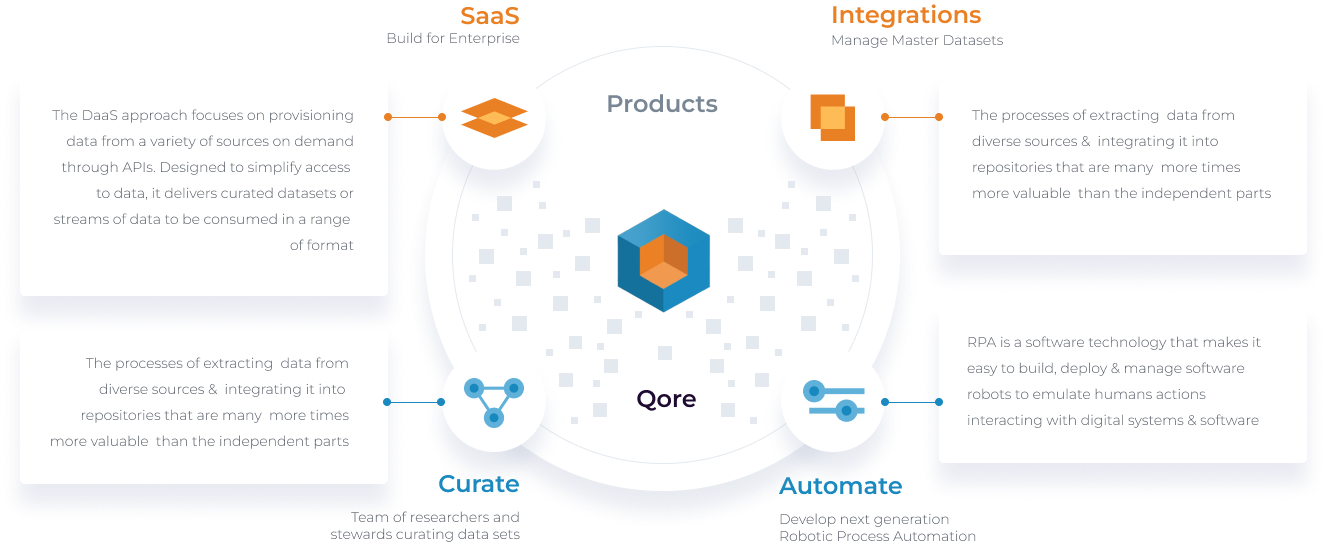
The DaaS approach focuses on provisioning data from a variety of sources on demand through APIs. Designed to simplify access to data, it delivers curated datasets or streams of data to be consumed in a range of format
RPA is a software technology that makes it easy to build, deploy & manage software robots to emulate humans actions interacting with digital systems & software
Data integration is the practice of consolidating data from disparate sources into a single dataset with the ultimate goal of providing users with consistent access & delivery of data across a spectrum of subjects & structure types
Introducing the
Qore Data Factory
The combination of automation and researchers allows us to reach up to 99% data accuracy for all our published data
Curate
Team of researchers and stewards curating data sets
The processes of extracting data from diverse sources & integrating it into repositories that are many more times more valuable than the independent parts
Automate
Develop next generation Robotic Process Automation
RPA is a software technology that makes it easy to build, deploy & manage software robots to emulate humans actions interacting with digital systems & software
SaaS
Build for Enterprise
The DaaS approach focuses on provisioning data from a variety of sources on demand through APIs. Designed to simplify access to data, it delivers curated datasets or streams of data to be consumed in a range of format
Integrations
Manage Master Datasets
Data integration is the practice of consolidating data from disparate sources into a single dataset with the ultimate goal of providing users with consistent access & delivery of data across a spectrum of subjects & structure types
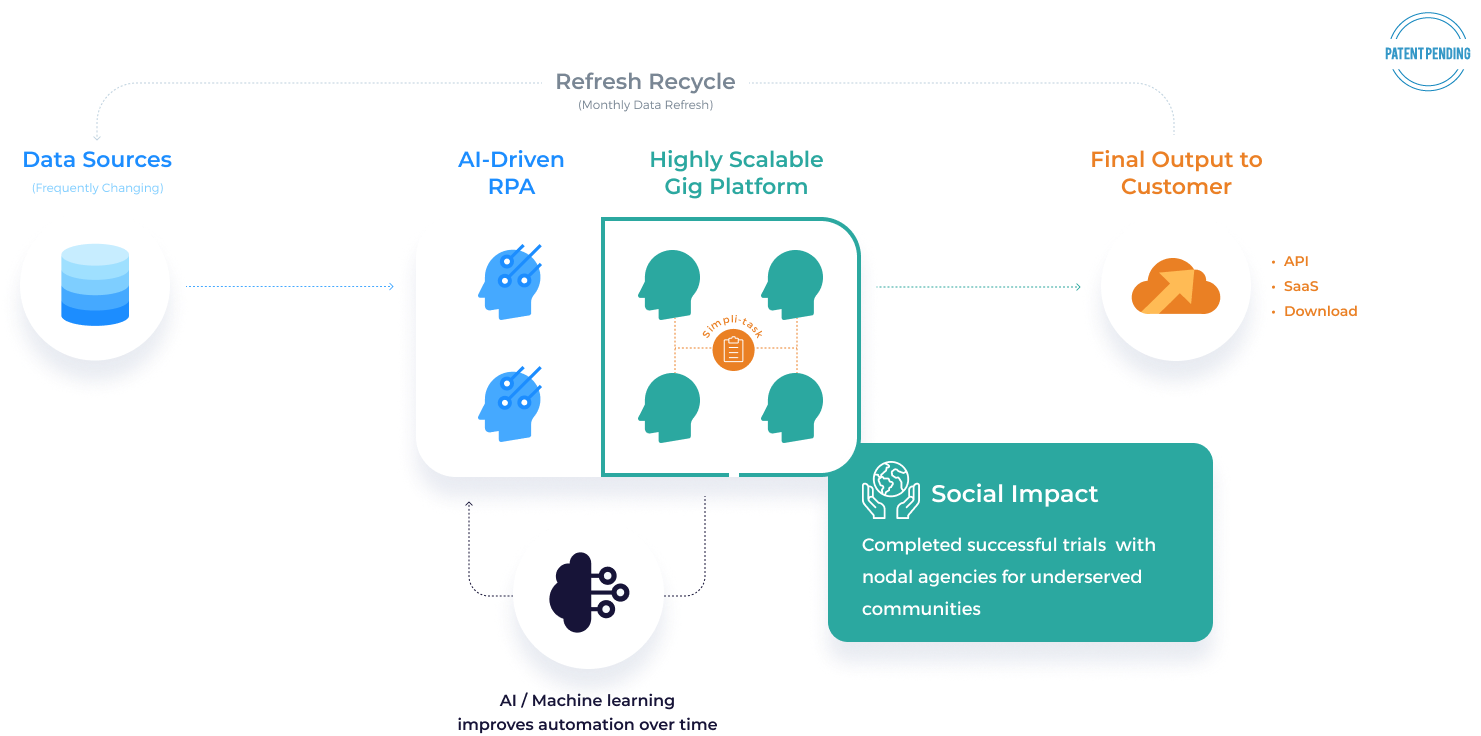
Data Assembly Line (DAL)
How we build data products



Combining Technology, Collaboration & Empathy
Data Categories
-
Facts
Fact data describe the factual information pertaining a dataset.
Examples include facts about businesses (annual revenue, no. of employees, country origin, location of offices etc.)
Because these data are not widely used by multiple businesses, it is usually customized (prepared only upon request).
Fact data tend to come together with a master dataset.
-
Master
Master data describe the people, places, and things that are involved in an organization’s business.
Examples include people (customers, employees, vendors, suppliers etc.), places (locations, sales territories, offices etc.), and things (accounts, products, assets, document sets etc.).
Because these data tend to be used by multiple business processes and IT systems, standardizing master data formats and synchronizing values are critical for successful system integration.
Master data tend to be grouped into master records, which may include associated reference data. An example of associated reference data is a state field within an address in a customer master record.
-
Reference
Reference data are sets of values or classification schemas that are referred to by systems, applications, data stores, processes, and reports, as well as by transactional and master records.
Examples include lists of valid values, code lists, status codes, state abbreviations, demographic fields, flags, product types, gender, chart of accounts, and product hierarchy.
Standardized reference data are key to data integration and interoperability and facilitate the sharing and reporting of information. Reference data may be used to differentiate one type of record from another for categorization and analysis, or they may be a significant fact such as country, which appears within a larger information set such as address.
Organizations often create internal reference data to characterize or standardize their own information. Reference data sets are also defined by external groups, such as government or regulatory bodies, to be used by multiple organizations. For example, currency codes are defined and maintained by ISO
Introducing the Qore Data Factory
Introducing the Qore Data Factory

Saas
Build for Enterprise

Integration
Manage Master Datasets
Curate
Team of researchers and stewards curating data sets
Automate
Develop next generation Robotic Process Automation
Data Assembly Line (DAL)
How we build data products
3 Core Components

AI

Machine Learning

Gig Platform
Combining Technology, Collaboration & Empathy
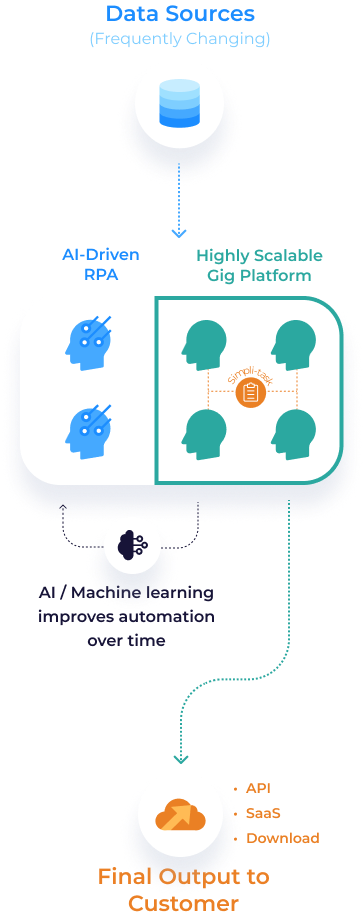
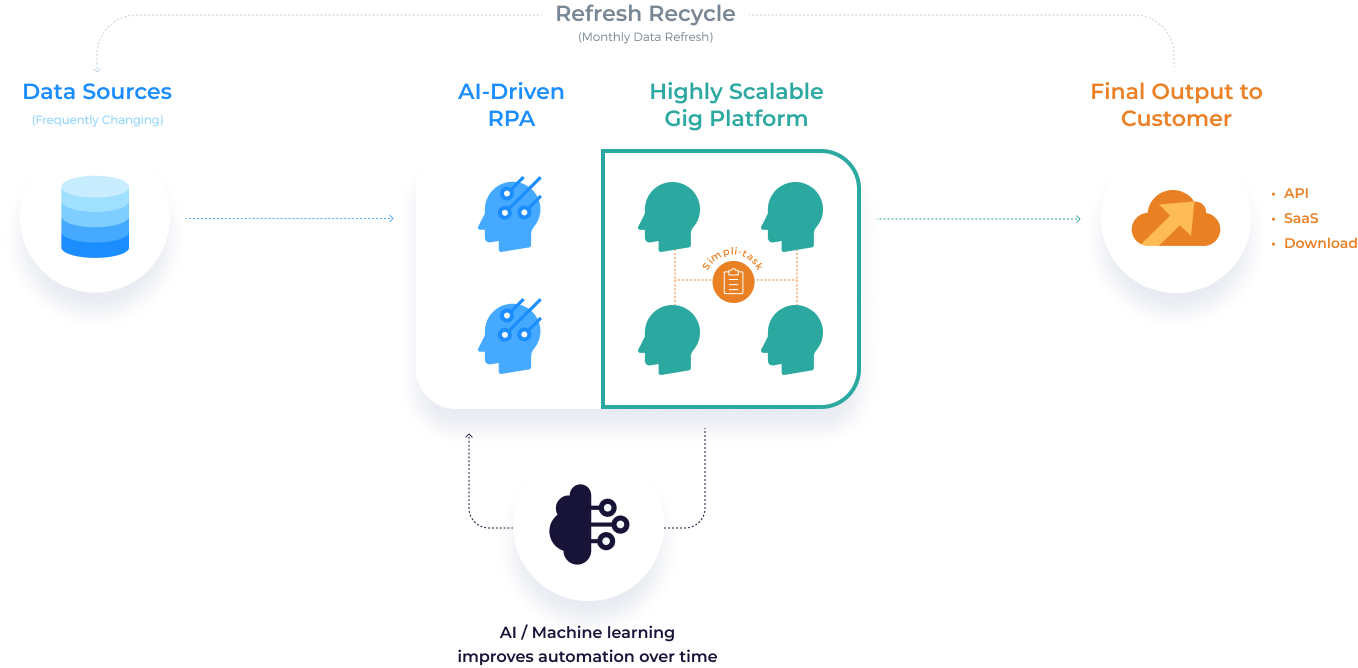
Data Assembly Line (DAL)
How we build data products



Combining Technology, Collaboration & Empathy
Data Products
Data Access Models
Point-in-time download
Data will be updated as of time of download (constant data refresh/ updates will not be provided)
API access
API stands for Application Programming Interface, it is a software-to-software interface. APIs provide a secure & standardized way for applications to with one another to deliver information/ functionality - allowing data to be constantly updated & refreshed
SaaS no-code
Using a no-code SaaS platform allows both developers and non-developers to rapidly build features without the need for coding - they can just drag and drop modules into a logical chain
Data Access Models
Point-in-time download
Data will be updated as of time of download (constant data refresh/ updates will not be provided)
API access
API stands for Application Programming Interface, it is a software-to-software interface. APIs provide a secure & standardized way for applications to with one another to deliver information/ functionality - allowing data to be constantly updated & refreshed
SaaS no-code
Using a no-code SaaS platform allows both developers and non-developers to rapidly build features without the need for coding - they can just drag and drop modules into a logical chain
Data Access Models
Point-in-time download
Data will be updated as of time of download (constant data refresh/ updates will not be provided)
API access
API stands for Application Programming Interface, it is a software-to-software interface. APIs provide a secure & standardized way for applications to with one another to deliver information/ functionality - allowing data to be constantly updated & refreshed
SaaS no-code
Using a no-code SaaS platform allows both developers and non-developers to rapidly build features without the need for coding - they can just drag and drop modules into a logical chain
Data Access Models
Point-in-time download
Data will be updated as of time of download (constant data refresh/ updates will not be provided)
API access
API stands for Application Programming Interface, it is a software-to-software interface. APIs provide a secure & standardized way for applications to with one another to deliver information/ functionality - allowing data to be constantly updated & refreshed
SaaS no-code
Using a no-code SaaS platform allows both developers and non-developers to rapidly build features without the need for coding - they can just drag and drop modules into a logical chain
Data Access Models
Point-in-time download
Data will be updated as of time of download (constant data refresh/ updates will not be provided)
API access
API stands for Application Programming Interface, it is a software-to-software interface. APIs provide a secure & standardized way for applications to with one another to deliver information/ functionality - allowing data to be constantly updated & refreshed
SaaS no-code
Using a no-code SaaS platform allows both developers and non-developers to rapidly build features without the need for coding - they can just drag and drop modules into a logical chain
Data Products

Data Access Models

Point-in-time-download

API Access

SaaS no-code
Data Categories
Fact
Fact data describe the factual information pertaining a dataset.
Examples include facts about businesses (annual revenue, no. of employees, country origin, location of offices etc.)
Because these data are not widely used by multiple businesses, it is usually customized (prepared only upon request).
Fact data tend to come together with a master dataset.
Master
Master data describe the people, places, and things that are involved in an organization’s business.
Examples include people (customers, employees, vendors, suppliers etc.), places (locations, sales territories, offices etc.), and things (accounts, products, assets, document sets etc.).
Because these data tend to be used by multiple business processes and IT systems, standardizing master data formats and synchronizing values are critical for successful system integration.
Master data tend to be grouped into master records, which may include associated reference data. An example of associated reference data is a state field within an address in a customer master record.

Reference
Reference data are sets of values or classification schemas that are referred to by systems, applications, data stores, processes, and reports, as well as by transactional and master records.
Examples include lists of valid values, code lists, status codes, state abbreviations, demographic fields, flags, product types, gender, chart of accounts, and product hierarchy.
Standardized reference data are key to data integration and interoperability and facilitate the sharing and reporting of information. Reference data may be used to differentiate one type of record from another for categorization and analysis, or they may be a significant fact such as country, which appears within a larger information set such as address.
Organizations often create internal reference data to characterize or standardize their own information. Reference data sets are also defined by external groups, such as government or regulatory bodies, to be used by multiple organizations. For example, currency codes are defined and maintained by ISO
Sample Data Products
Data Access Models
Point-in-time download
Data will be updated as of time of download (constant data refresh/ updates will not be provided)
API access
API stands for Application Programming Interface, it is a software-to-software interface. APIs provide a secure & standardized way for applications to with one another to deliver information/ functionality - allowing data to be constantly updated & refreshed
SaaS no-code
Using a no-code SaaS platform allows both developers and non-developers to rapidly build features without the need for coding - they can just drag and drop modules into a logical chain
Data Categories
-
Facts
Fact data describe the factual information pertaining a dataset.
Examples include facts about businesses (annual revenue, no. of employees, country origin, location of offices etc.)
Because these data are not widely used by multiple businesses, it is usually customized (prepared only upon request).
Fact data tend to come together with a master dataset.
-
Master
Master data describe the people, places, and things that are involved in an organization’s business.
Examples include people (customers, employees, vendors, suppliers etc.), places (locations, sales territories, offices etc.), and things (accounts, products, assets, document sets etc.).
Because these data tend to be used by multiple business processes and IT systems, standardizing master data formats and synchronizing values are critical for successful system integration.
Master data tend to be grouped into master records, which may include associated reference data. An example of associated reference data is a state field within an address in a customer master record.
-
Reference
Reference data are sets of values or classification schemas that are referred to by systems, applications, data stores, processes, and reports, as well as by transactional and master records.
Examples include lists of valid values, code lists, status codes, state abbreviations, demographic fields, flags, product types, gender, chart of accounts, and product hierarchy.
Standardized reference data are key to data integration and interoperability and facilitate the sharing and reporting of information. Reference data may be used to differentiate one type of record from another for categorization and analysis, or they may be a significant fact such as country, which appears within a larger information set such as address.
Organizations often create internal reference data to characterize or standardize their own information. Reference data sets are also defined by external groups, such as government or regulatory bodies, to be used by multiple organizations. For example, currency codes are defined and maintained by ISO